Google Ads (formerly known as Google AdWords) is one of the most popular PPC advertising platforms. Businesses use it to target high‑intent searchers, drive website traffic and generate leads or product sales. But with rising costs per click and increasing competition, many marketers ask: Is Google Ads worth it?
This article demystifies Google Ads by explaining how the platform works, why it still matters in 2025, and how businesses can determine whether it’s a good fit for their marketing mix. We’ll look at current ROI data, outline best practices, highlight common pitfalls and share some real‑world case studies. You’ll also find answers to frequently asked questions and recommended tools to help you get started.
What Is Google Ads?
Google Ads is Google’s pay‑per‑click advertising platform. Despite it being labeled as a pay-per-click platform, you can also pay by impressions, video views, or viewable impressions too with proper settings. Advertisers bid on keywords to display text ads, image ads, product listings (in Google Shopping) or video ads across Google Search, YouTube, Gmail and partner sites.
With most bidding strategies, you only pay when someone clicks your ad or watches your video (for a varying minimum amount of time based on the placement and content length), making it a flexible way to drive qualified traffic.
In the broader digital‑marketing landscape, Google Ads represents one channel (containing a diverse set of placements and platforms – like search, YouTube, third-party websites, and Gmail) alongside organic search (SEO), social media, email marketing and fast-growing platforms like TikTok.
While many other channels focus on building long‑term brand authority or community through targeting based purely on interests, paid search excels at capturing immediate demand — people actively searching for specific keywords and phrases with purchase intent. When implemented strategically, it can deliver a steady pipeline of bottom-funnel leads or sales.
Why Google Ads Matters Today
Advertisers Still See Strong Returns
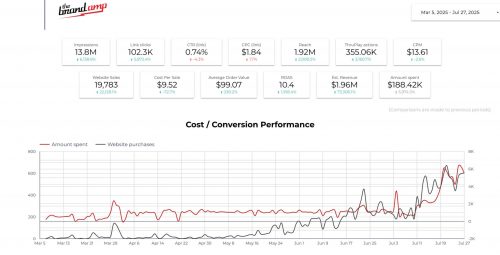
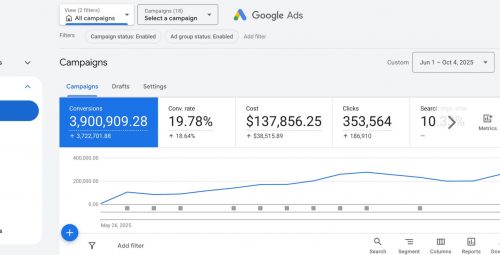
The digital advertising market continues to grow, and recent statistics show that Google Ads remains a strong investment. According to multiple 2025 benchmark reports compiled by DemandSage and other analytics firms, businesses using Google Ads see an average return of $2 in revenue for every $1 spent (demandsage.com). While this figure may fluctuate by industry and campaign quality, it illustrates that well‑managed accounts still produce positive returns.
Rising Competition and Costs
However, competition for top positions is fierce. Search engine marketing experts note that average cost‑per‑click (CPC) has risen across numerous verticals, driven by more advertisers entering the auctions. In some industries CPCs increased by double‑digit percentages year over year, making efficient bidding and targeting more important than ever (demandsage.com).
Keeping an eye on your Auction Insights report is an important way to keep a pulse on competitors that are bidding on your keywords. Advertisers must continuously optimize keyword lists, bidding strategies, ad copy and landing pages to maintain profitability.
Privacy, AI and Automation Trends
Privacy regulations and the deprecation of third‑party cookies have forced digital advertising tactics to adapt. At the same time, Google’s automated bidding and machine‑learning tools are improving at predicting user intent. Advertisers who leverage first‑party data and embrace automation while maintaining regular oversight can gain a competitive edge. Google Ads remains one of the few channels where you can adjust budgets and targeting in real time, giving your business a critical advantage in a rapidly changing environment.
How Google Ads Works: Core Components
Google Ads uses an auction to determine when and where your paid ads appear. Understanding these components helps you estimate costs and results:
1. Keyword Bidding
For search ads, you select keywords or search phrases relevant to your business and assign a maximum bid (if you’re using using a max click bidding strategy this is the most you’re willing to pay per click). Google’s algorithm considers your bid along with Quality Score (ad relevance, expected click‑through rate and landing page experience) to determine your ad’s placement.
2. Ad Formats
You can choose from several ad types:
| Ad Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Search Ads | Text ads appearing on Google Search results pages. Ideal for capturing high‑intent queries. |
| Display Ads | Image or responsive ads shown across Google’s Display Network of millions of sites. Great for brand awareness and remarketing. |
| Shopping Ads | Product images and prices appearing in Shopping results; perfect for e‑commerce. |
| Video Ads | Video spots on YouTube or video partners. Useful for storytelling and reach. |
3. Audience & Targeting Options
Besides keywords, Google lets you target audiences based on location, device, demographics, interests, customer lists, remarketing lists and more. Smart Bidding strategies (Target ROAS, Target CPA, Maximize Conversions) use machine learning to automate bid adjustments in real time based on conversion data.
Best Practices and Strategies
1. Align Ads With Business Goals
Set clear objectives, such as lead generation, product sales or brand awareness, and choose the appropriate campaign type. For example, a B2B company might prioritize Google Search campaigns to capture high-intent leads, while an e-commerce brand might lean on Performance Max or Shopping campaigns to sync with product feeds. Both aim to drive conversions, but each campaign type requires a distinct setup and optimization approach.
2. Optimize Keywords and Negative Lists
Conduct keyword research using tools like SEMrush and Google Keyword Planner. Select exact or phrase match terms to capture high‑value queries, and continuously refine negative keywords to exclude irrelevant clicks. This reduces wasted spend.
3. Create Compelling Ad Copy
Write headlines that include your target keywords and highlight your brand’s benefit or unique selling proposition. Use strong ad extensions (callouts, sitelinks, structured snippets, etc.) to add credibility and improve click‑through rate (CTR).
4. Enhance Landing Pages
Direct users to pages that match your ad’s promise. Fast‑loading, mobile‑friendly pages with clear calls‑to‑action (CTAs) improve Quality Score and conversion rates. Include target keywords on your landing page. If you need inspiration, our case study on Winter Fest OC integrated optimized landing pages with well-placed paid media, driving a 25% increase in ticket sales.
5. Use First‑Party Data and Automation
Upload customer lists or use The Brand Amp’s digital strategy services to build highly-tailored audiences based on your CRM, brand engagement or site activity. Then test Smart Bidding to optimize bids for conversions or ROAS. Provide sufficient conversion data (usually 30+ conversions per month) to allow the algorithm to learn effectively.
6. Monitor and Iterate
Review campaign performance regularly and adjust accordingly. Look at click‑through rates, conversion rates and ROAS or cost per acquisition (CPA) to see whether your ads are profitable. Pause underperforming keywords, test new creative, refresh ad copy or landing pages. Combine Auction Insights (see our Auction Insights guide) with conversion data to understand competitive dynamics and where you need to adjust bids or budgets.
Tools & Resources
- Google Analytics 4 (GA4) – Closely tracks user behavior on your site and ties it to ad campaigns.
- Looker Studio – Connects Google Ads, GA4 and other data sources to visualize performance trends.
- Keyword Planner – Estimates search volume and suggests keywords.
- Microsoft Clarity – Easily monitor user interactions on your landing pages to determine performance.
- Auction Insights – Shows which advertisers appear in the same auctions and provides metrics like impression share and outranking rate. (See our Auction Insights article for a deep dive.)
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Relying solely on high volume keywords – These often attract broad traffic with lower conversion rates. Balance high‑volume terms with long‑tail keywords.
- Ignoring negative keywords – Without a robust negative list, you’ll likely pay for irrelevant clicks.
- Overlooking mobile optimization – Mobile users may behave differently; ensure ads and landing pages are mobile friendly.
- Not properly tracking conversions – Without conversion tracking or revenue data imported from your CRM/e‑commerce platform, you cannot optimize for profitability.
- Failing to test – Continual A/B testing of ad copy, landing pages and bidding strategies is essential to find what works best for your business.
Real‑World Case Study: KT Tape
One of The Brand Amp’s clients, KT Tape®, wanted to boost e‑commerce sales and brand awareness for its kinesiology tape products. We combined SEO, paid media, conversion rate optimization (CRO) and PR. The integrated campaign delivered 100 million impressions, increased ROAS by 18% and drove 7.5 million retail store visits (thebrandamp.com).
Paid search was a key pillar in the strategy, targeting high‑intent keywords and retargeting site visitors. By focusing on profitability metrics and optimizing targeting, creative and ad copy, the campaign generated more results without increasing ad spend. For a full overview, see our KT Tape case study.
Conclusion & Key Takeaways
Google Ads remains a valuable channel when managed thoughtfully. However, rising competition and costs mean that simply launching a campaign is not a guarantee of success. Effective campaigns align ads with business goals, use intentional targeting, create compelling copy and ongoing optimizations. They leverage first‑party data and automation while monitoring ad performance closely to make every dollar work harder.
If you’re still wondering whether Google Ads is worth it for your business, start with a small test budget and track results carefully. Or connect with The Brand Amp’s paid media experts, we are happy to look at your existing campaigns and build a strategy tailored to your goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is advertising on Google worth it for small businesses?
Yes, when targeted carefully. Small businesses with clear goals and defined audiences can gain quick visibility by bidding on specific keywords. Starting with a modest budget and using strategic location targeting and negative keywords helps control costs. Monitoring performance is crucial with proper tracking and optimizations in place.
2. How long does it take to see results from Google Ads?
Results can appear quickly, but significant optimizations usually take a few weeks. You need enough data to evaluate which keywords and ads convert. Continual testing and optimization improve results over time.
3. What budget do I need to start?
There’s no universal minimum. It depends largely on your audience size. Most advertisers start with a few thousand dollars per month to start and gather data, then scale up marketing budgets that prove profitable. Think of it as an investment in data collection as much as immediate sales.
4. Should I use Google Ads or focus on SEO?
Ideally, both. SEO builds long‑term organic visibility, while Google Ads delivers immediate traffic. Running both channels together can reveal which keywords convert best, informing your broader marketing strategy and unlocking higher overall performance in the longrun.
5. How can I track the ROI of Google Ads campaigns?
Implement conversion tracking in Google Ads and GA4. Assign values to leads or purchases, then calculate return on ad spend (ROAS) by dividing total conversion value by total ad spend. Look at profitability, not just clicks.
6. Where can I learn more about PPC best practices?
Check out our digital marketing blog for more articles on PPC strategy. Additionally, Google’s Skillshop offers free courses on search and display advertising.
Note: ROI figures and statistics referenced here are based on 2025 benchmark reports; always check the latest data to ensure they remain current.